Inhaled Treprostinil is the only FDA approved therapy for PH-ILD
IN A PIVOTAL PHASE 3 TRIAL, PATIENTS WITH PH-ILD TREATED WITH INHALED TREPROSTINIL SOLUTION HAD A SIGNIFICANT IMPROVEMENT IN 6MWD1,2
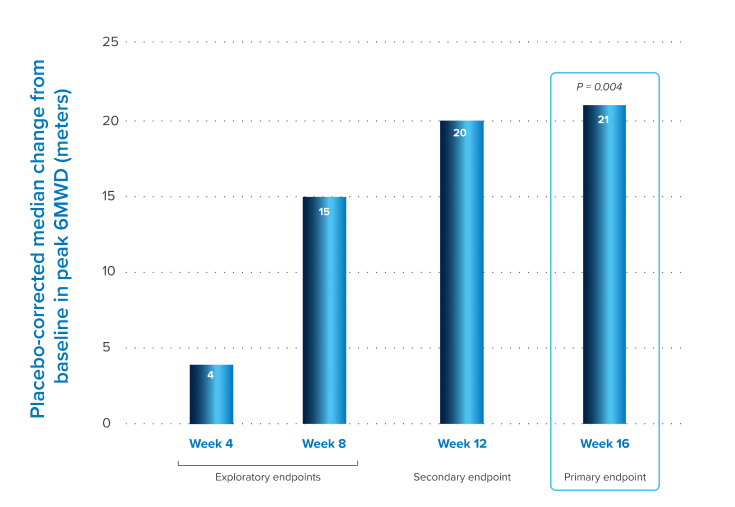
Data shown are the Hodges-Lehmann placebo-corrected median difference for patients treated with inhaled treprostinil solution.1
Treatment with inhaled treprostinil solution did not worsen pulmonary function, and fewer patients had exacerbated underlying lung disease2
-
16-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 326 patients with
PH-ILD1,2
- n = 163 inhaled treprostinil solution and n = 163 placebo
- ILD subtypes: 28% IPF, 25% CPFE, 22% CTD, 17% other IIP, 8% CHP/occupational/other1,2
- Primary endpoint: Change in 6MWD at peak exposure (10-60min post-dose)
- Secondary endpoint: Time to clinical worsening
Starting dose of inhaled treprostinil solution was 3 breaths QID. Dose escalations (1 breath QID) were permitted every ≥3 days, with a target maintenance dose of 9 breaths QID and a maximum permitted dose of 12 breaths QID, as clinically tolerated.1,2
Time to clinical worsening was evaluated from the time of randomization until the patient's withdrawal from the study due to one of the following events: hospitalization for a cardiopulmonary indication, study disease-related decrease in 6MWD of >15% from baseline on 2 consecutive occasions measured ≥24 hours apart, death from any cause, or lung transplantation.1
QID = four times daily.
DURING THE 16 WEEK STUDY, INHALED TREPROSTINIL SOLUTION REDUCED THE RISK OF A CLINICAL WORSENING EVENT BY 39%1
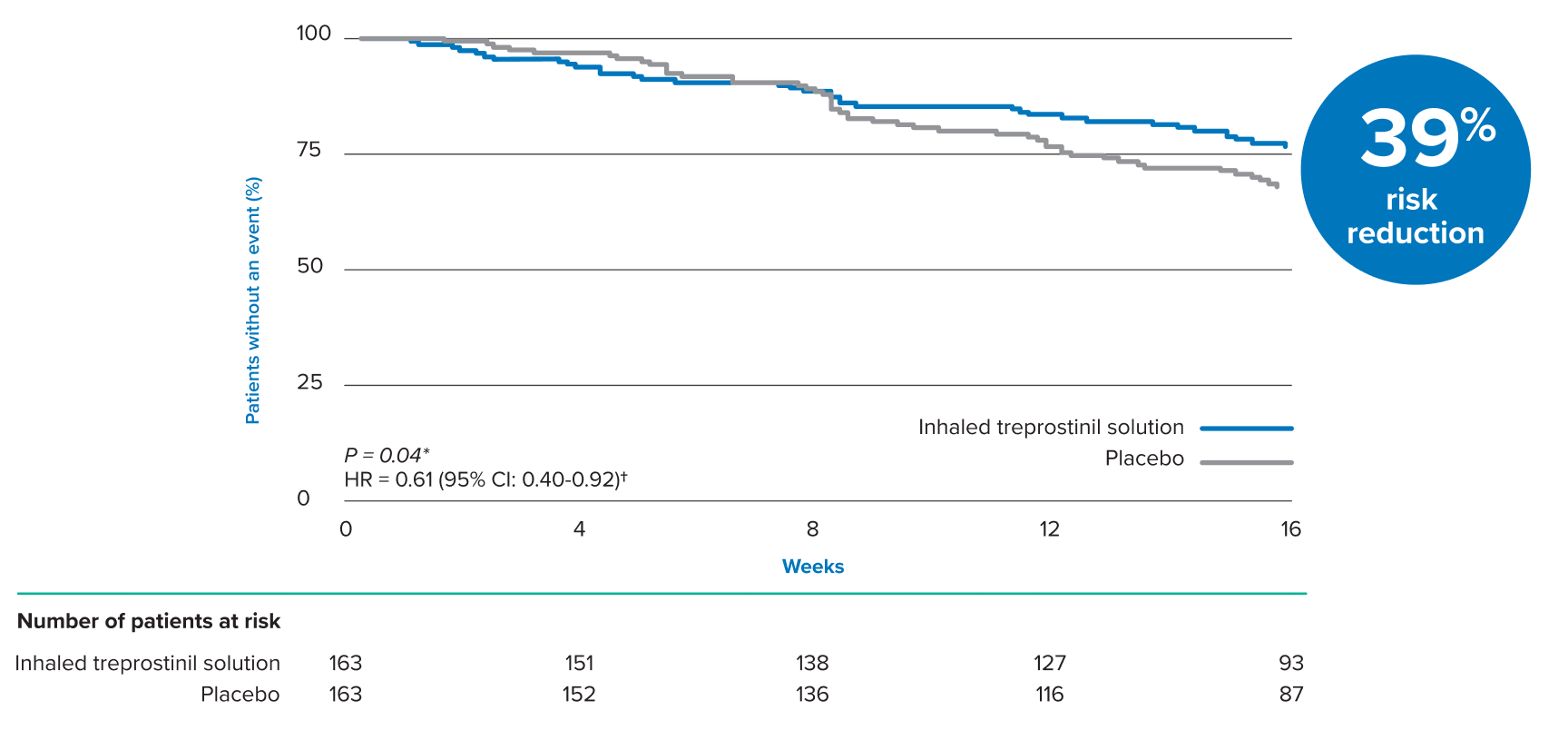
- Hospitalization due to a cardiopulmonary indication (11% inhaled treprostinil solution vs 14.7% placebo)
- Decrease in 6MWD >15% from baseline directly related to PH-ILD (8% inhaled treprostinil solution vs 16% placebo)
- Death (all causes) (2.5% inhaled treprostinil solution vs 2.5% placebo)
- Lung transplantation (1.2% inhaled treprostinil solution vs 0% placebo)
YUTREPIA BUILDS UPON THE ESTABLISHED SAFETY AND EFFICACY OF INHALED TREPROSTINIL SOLUTION1,4,5
INSPIRE was a 2-month, Phase 3, open-label, multicenter trial that studied YUTREPIA in 121 patients with PAH who were NYHA FC II or III at baseline1,5
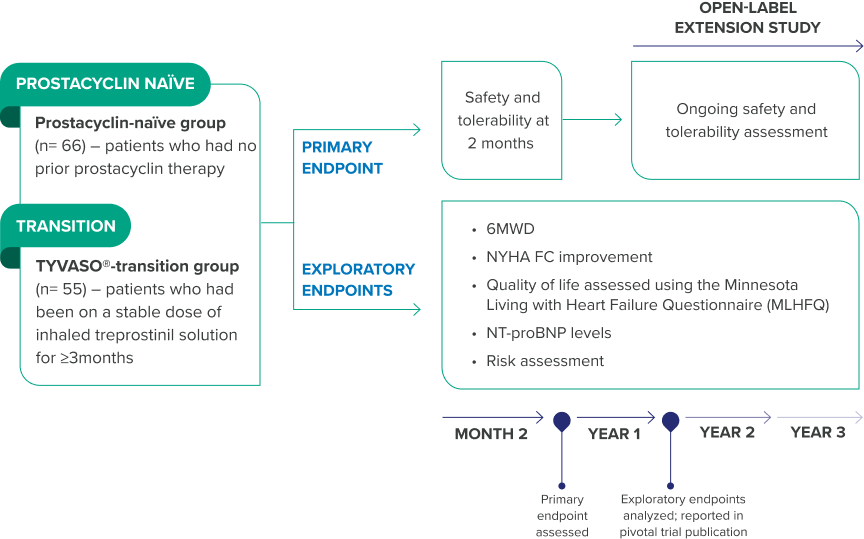
Most patients received background oral PAH therapy, with 71% on dual therapy (ERA + PDE-5i or sGC), 25% on monotherapy (ERA, PDE-5i, or sGC), and 4% receiving no other therapy.5
ERA = endothelin receptor antagonist; NYHA FC = New York Heart Association functional class; PDE-5i = phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor; sGC = soluble guanylate cyclase agonist
YUTREPIA MADE IT POSSIBLE TO TITRATE TO HIGHER THERAPEUTIC DOSES1,5
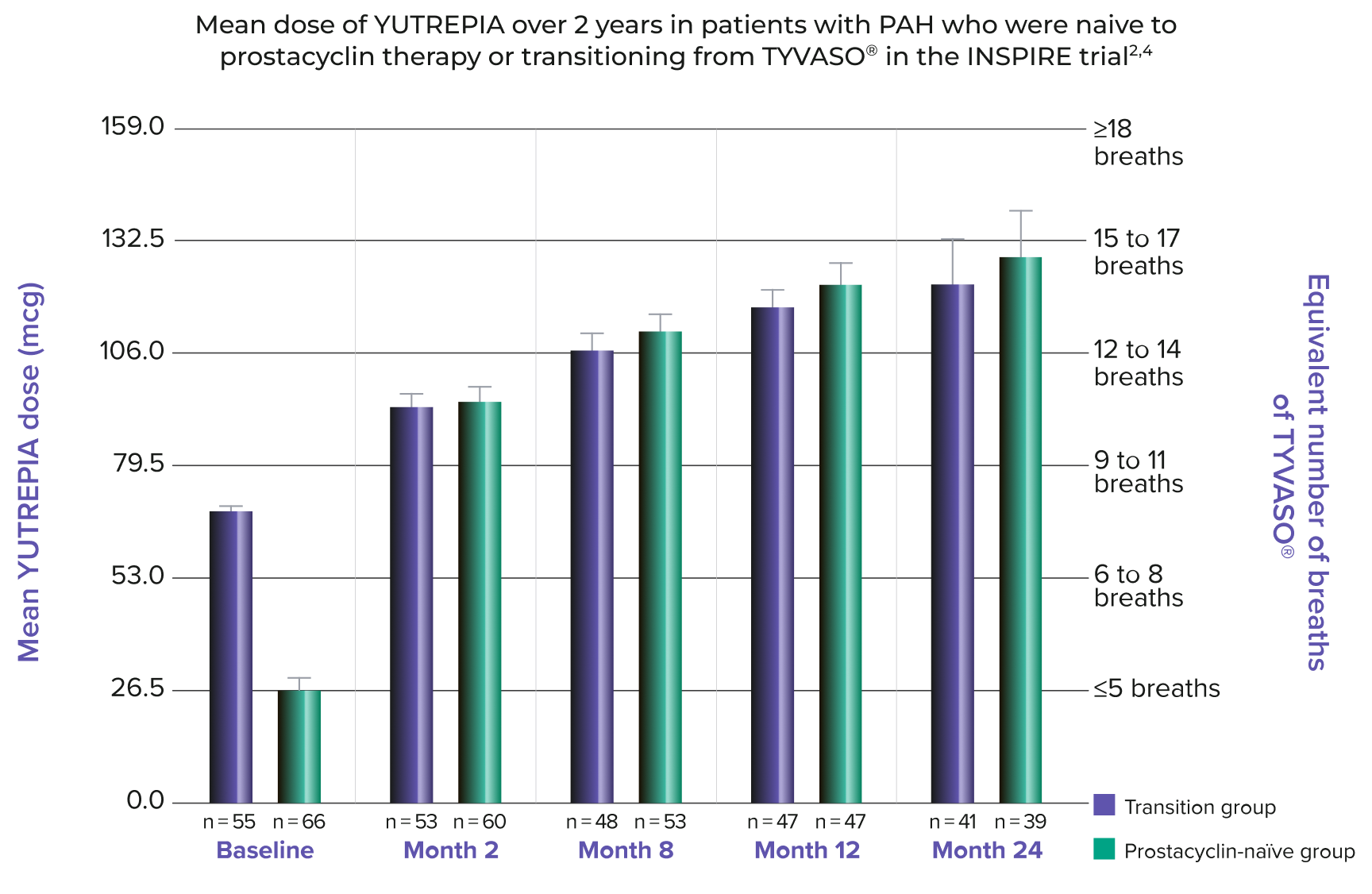
DOSES AT 1 YEAR1,6,7:
- 41.5% (n = 39/94) of patients reached a dose of ≥132.5 mcg (equivalent to ≥15 breaths of TYVASO®)
- 3 patients reached a dose of 212 mcg (equivalent to ≥24 breaths of TYVASO®)
DOSES AT 2 YEARS1,6,7:
- 32.5% (n = 26/80) of patients reached a dose of ≥159 mcg (equivalent to ≥18 breaths of TYVASO®)
- 1 patient reached 238.5 mcg (equivalent to ≥27 breaths of TYVASO®)
INDICATION AND IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH; WHO Group 1) to improve exercise ability. Studies establishing effectiveness predominately included patients with NYHA Functional Class III symptoms and etiologies of idiopathic or heritable PAH (56%) or PAH associated with connective tissue diseases (33%).
- Pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease (PH-ILD; WHO Group 3) to improve exercise ability. The study establishing effectiveness predominately included patients with etiologies of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP) (45%) inclusive of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema (CPFE) (25%), and WHO Group 3 connective tissue disease (22%).
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Treprostinil is a pulmonary and systemic vasodilator. In patients with low systemic arterial pressure, treatment with treprostinil may produce symptomatic hypotension.
- Treprostinil inhibits platelet aggregation and increases the risk of bleeding.
- Co-administration of a cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C8 enzyme inhibitor (e.g., gemfibrozil) may increase exposure (both Cmax and AUC) to treprostinil. Co-administration of a CYP2C8 enzyme inducer (e.g., rifampin) may decrease exposure to treprostinil. Increased exposure is likely to increase adverse events associated with treprostinil administration, whereas decreased exposure is likely to reduce clinical effectiveness.
- Like other inhaled prostaglandins, YUTREPIA may cause acute bronchospasm. Patients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or other bronchial hyperreactivity, are at increased risk for bronchospasm. Ensure that such patients are treated optimally for reactive airway disease prior to and during treatment with YUTREPIA.
DRUG INTERACTIONS/SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- The concomitant use of treprostinil with diuretics, antihypertensives, or other vasodilators may increase the risk of symptomatic hypotension.
- Human pharmacokinetic studies with an oral formulation of treprostinil (treprostinil diolamine) indicated that co-administration of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C8 enzyme inhibitor, gemfibrozil, increases exposure (both Cmax and AUC) to treprostinil. Co-administration of the CYP2C8 enzyme inducer, rifampin, decreases exposure to treprostinil. It is unclear if the safety and efficacy of treprostinil by the inhalation route are altered by inhibitors or inducers of CYP2C8.
- Limited case reports of treprostinil use in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug-associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. However, pulmonary arterial hypertension is associated with an increased risk of maternal and fetal mortality. There are no data on the presence of treprostinil in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production.
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
- Placebo-controlled clinical studies of treprostinil inhalation solution did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. The open label INSPIRE study in patients with PAH included 28 patients aged 65 and over in which no age-related differences were noted. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of hepatic, renal, or cardiac dysfunction, and of concomitant diseases or other drug therapy.
- Uptitrate slowly when treating patients with hepatic insufficiency because of the risk of an increase in systemic exposure which may lead to an increase in dose-dependent adverse effects. Treprostinil has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic insufficiency.
- No dose adjustments are required in patients with renal impairment. Treprostinil is not cleared by dialysis.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- PAH (WHO Group 1): The safety and tolerability of YUTREPIA was evaluated in an open label study (INSPIRE) of 121 patients with PAH (WHO Group 1 and NYHA Functional Class II [80 patients] and Class III [41 patients]) followed for up to 2 months. The most commonly reported adverse reactions included cough, headache, throat irritation, dizziness, which are known side effects of treprostinil inhalation solution. The adverse reactions in the INSPIRE study were consistent with those observed in previous studies of inhaled treprostinil.
- PH-ILD (WHO Group 3): In a 16-week, placebo-controlled study of 326 patients with PH-ILD (WHO Group 3), adverse reactions with inhaled treprostinil were similar to the experience in studies of PAH.
Please see Full Prescribing Information for YUTREPIA.
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH; WHO Group 1) to improve exercise ability. Studies establishing effectiveness predominately included patients with NYHA Functional Class III symptoms and etiologies of idiopathic or heritable PAH (56%) or PAH associated with connective tissue diseases (33%).
- Pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease (PH-ILD; WHO Group 3) to improve exercise ability. The study establishing effectiveness predominately included patients with etiologies of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP) (45%) inclusive of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema (CPFE) (25%), and WHO Group 3 connective tissue disease (22%).
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Treprostinil is a pulmonary and systemic vasodilator. In patients with low systemic arterial pressure, treatment with treprostinil may produce symptomatic hypotension.
- Treprostinil inhibits platelet aggregation and increases the risk of bleeding.
- Co-administration of a cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C8 enzyme inhibitor (e.g., gemfibrozil) may increase exposure (both Cmax and AUC) to treprostinil. Co-administration of a CYP2C8 enzyme inducer (e.g., rifampin) may decrease exposure to treprostinil. Increased exposure is likely to increase adverse events associated with treprostinil administration, whereas decreased exposure is likely to reduce clinical effectiveness.
- Like other inhaled prostaglandins, YUTREPIA may cause acute bronchospasm. Patients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or other bronchial hyperreactivity, are at increased risk for bronchospasm. Ensure that such patients are treated optimally for reactive airway disease prior to and during treatment with YUTREPIA.
DRUG INTERACTIONS/SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- The concomitant use of treprostinil with diuretics, antihypertensives, or other vasodilators may increase the risk of symptomatic hypotension.
- Human pharmacokinetic studies with an oral formulation of treprostinil (treprostinil diolamine) indicated that co-administration of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C8 enzyme inhibitor, gemfibrozil, increases exposure (both Cmax and AUC) to treprostinil. Co-administration of the CYP2C8 enzyme inducer, rifampin, decreases exposure to treprostinil. It is unclear if the safety and efficacy of treprostinil by the inhalation route are altered by inhibitors or inducers of CYP2C8.
- Limited case reports of treprostinil use in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug-associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. However, pulmonary arterial hypertension is associated with an increased risk of maternal and fetal mortality. There are no data on the presence of treprostinil in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production.
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
- Placebo-controlled clinical studies of treprostinil inhalation solution did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. The open label INSPIRE study in patients with PAH included 28 patients aged 65 and over in which no age-related differences were noted. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of hepatic, renal, or cardiac dysfunction, and of concomitant diseases or other drug therapy.
- Uptitrate slowly when treating patients with hepatic insufficiency because of the risk of an increase in systemic exposure which may lead to an increase in dose-dependent adverse effects. Treprostinil has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic insufficiency.
- No dose adjustments are required in patients with renal impairment. Treprostinil is not cleared by dialysis.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- PAH (WHO Group 1): The safety and tolerability of YUTREPIA was evaluated in an open label study (INSPIRE) of 121 patients with PAH (WHO Group 1 and NYHA Functional Class II [80 patients] and Class III [41 patients]) followed for up to 2 months. The most commonly reported adverse reactions included cough, headache, throat irritation, dizziness, which are known side effects of treprostinil inhalation solution. The adverse reactions in the INSPIRE study were consistent with those observed in previous studies of inhaled treprostinil.
- PH-ILD (WHO Group 3): In a 16-week, placebo-controlled study of 326 patients with PH-ILD (WHO Group 3), adverse reactions with inhaled treprostinil were similar to the experience in studies of PAH.
Please see Full Prescribing Information for YUTREPIA.
References
- YUTREPIA. Prescribing information. Liquidia Technologies, Inc; 2025.
- Waxman A, Restrepo-Jaramillo R, Thenappan T, et al. Inhaled treprostinil in pulmonary hypertension due to interstitial lung disease. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(4):325-334. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2008470
- Waxman A, Restrepo-Jaramillo R, Thenappan T, et al. Inhaled treprostinil in pulmonary hypertension due to interstitial lung disease. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(4)(suppl):1-30. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2008470
- West N, Smoot K, Patzlaff N, Miceli M, Waxman A. Plain language summary of the INCREASE study: inhaled treprostinil (Tyvaso) for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension due to interstitial lung disease. Future Cardiol. 2023;19(5):229-239. doi:10.2217/fca-2022-0108
- Hill NS, Feldman JP, Sahay S, et al; INSPIRE study investigators. INSPIRE: safety and tolerability of inhaled Yutrepia (treprostinil) in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Pulm Circ. 2022;12(3):e12119. doi:10.1002/pul2.12119
- Data on file. Liquidia Technologies, Inc.
- Simon MA, Shapiro SM, Sahay S, et al. Clinical outcomes of YUTREPIA™ dose in 6MWD and quality of life. Poster presented at: CHEST 2022 Annual Meeting; October 16-19, 2022; Nashville, TN.